A report recently published in the American Journal of Epidemiology suggested that smoking increased the risk of developing non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) by more than three times.
美国《流行病学杂志》最近发表的一份报告表明,吸烟使人们患非胰岛
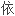
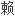 型糖
型糖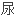 病的
病的
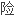
 加了3倍多。
加了3倍多。
声明:以上例句、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。