It is well established that the cardial contraction is initiated when an action potential depolarizes the sarcolemma.
已经确证,心
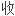
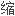 始
始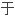 动
动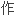

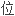 使
使 膜去极化。
膜去极化。
声明:以上例句、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。
 血管
血管  血管
血管  血管
血管  血管
血管 

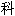

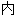
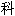

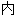
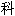

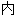
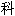

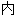
 血管
血管  血管
血管  理学篇
理学篇  血管
血管  血管
血管