The diagnosis of hyperaldosteronism is mainly done by measuring levels of renin and aldosterone.
醛固

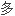 症的诊断主要通过测定肾素与醛固
症的诊断主要通过测定肾素与醛固 的水平来完成。
的水平来完成。
Individuals with hyperaldosteronism typically develop hypertension related symptoms like headaches and facial flushing, as well as hypokalemia related symptoms like constipation, weakness, and potentially changes in their heart rhythm.
醛固

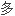 症患者通常会出现高血压相关症状,如头痛和面部潮红,以及低钾血症相关症状,如便秘、乏力与对心律的潜在影响。
症患者通常会出现高血压相关症状,如头痛和面部潮红,以及低钾血症相关症状,如便秘、乏力与对心律的潜在影响。
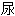
All that being said, in situations where somebody produces too much aldosterone, like primary hyperaldosteronism, then there's more potassium secretion by the principal cells and excreted, and therefore less potassium is retained, leading to hypokalemia.
说了这么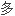 ,在某人产生了太
,在某人产生了太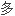 醛固
醛固 的情况下,比如原发
的情况下,比如原发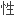 醛固
醛固

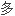 症,更
症,更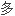 的钾被主细胞分泌并排泄,这意味着更少的钾被保留,导致了低钾血症。
的钾被主细胞分泌并排泄,这意味着更少的钾被保留,导致了低钾血症。
All right, as a quick recap, hyperaldosteronism is the chronic, excess secretion of aldosterone from the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal gland, and these high aldosterone levels can lead to hypokalemia, hypernatremia, hypertension, and a metabolic alkalosis.
得!简单回顾一下:醛固

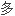 症是指肾上腺球状带长期分泌过
症是指肾上腺球状带长期分泌过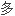 的醛固
的醛固 ;这些高醛固
;这些高醛固 水平可导致低钾血症、高钠血症、高血压与代谢
水平可导致低钾血症、高钠血症、高血压与代谢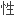 碱中毒。
碱中毒。