13 fatty acids components, 2 sterol and phytol ones were identified from R. dentatua L., amounting to 86.03% of the total constituents.
从齿果酸模中分离鉴定了13

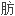 酸成分、2
酸成分、2 甾类成分和1
甾类成分和1 植醇,占色谱总
植醇,占色谱总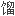 分出峰面积的86.03%。
分出峰面积的86.03%。
声明:以上例句、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。
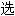
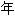 9月合集
9月合集 
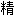
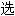
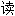
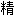
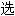
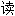
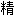
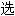
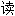
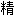
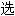
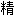
Benjamin Nettersheim, a geobiologist at the University of Bremen in Germany, Jochen Brocks, a palaeobiogeochemist at the Australian National University in Canberra, and their colleagues decided to focus on short-lived molecules that modern eukaryotes make while synthesizing sterols.
德国不莱梅大学的地球生物学家本杰明·内特谢姆、澳大利亚国立大学堪培拉分校的古生物地球化学家约翰·布洛克斯及其同事决定将重点放在现代真核生物合成类固醇时产生的短寿命分子上。