Objective To compare the effects of small-dose sufentanil and fentanyl on cardiovascular responses to laryngoscopic orotracheal intubation in children.
目的比较小剂量舒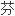
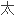
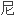 和枸橼酸
和枸橼酸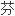
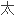
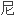 预防儿童
预防儿童
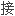
 镜经口气
镜经口气 插
插 心血
心血 反应的效果。
反应的效果。
声明:以上例句、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。