Objective To evaluate the histological characteristics of xenogeneic graft-versus-host disease(GVHD),and to differentiate it from the allogeneic GVHD.
目的了解异种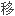
 物抗宿主病(GVHD)的组织学特点,与同种GVHD的区别及异种脾脏
物抗宿主病(GVHD)的组织学特点,与同种GVHD的区别及异种脾脏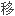
 的关系。
的关系。
声明:以上例句、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。
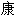
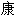
MSCs differentiate into adipocytes, osteocytes, chondrocytes, tenocytes, marrow stromal cells, muscle, and perhaps neuronal cells and are being used in early clinical trials to enhance bone marrow grafting and to suppress graft-versus-host disease in allogeneic bone marrow transplants.
MSCs分化成脂肪细胞,骨细胞,软骨细胞,肌腱细胞,骨髓基质细胞,肌肉和神经细胞,并用于早期临床试验,以增 骨髓移植和抑制同种异体骨髓移植中
骨髓移植和抑制同种异体骨髓移植中 移植物抗宿主病。
移植物抗宿主病。
If an antigen encounters a T cell, the T cell can multiply rapidly. These activated T cells engulf and digest the antigen, such as a cancer cell, virus, fungus, or bacterium. T cells also react to foreign tissues, such as skin grafts and transplanted organs.
如果抗原遇到T细胞,T细胞可迅速繁殖。这些活化 T细胞吞噬并消化抗原,例如癌细胞,病毒,真菌或细菌。 T细胞也会对外来组织起反应,例如皮肤移植物和移植
T细胞吞噬并消化抗原,例如癌细胞,病毒,真菌或细菌。 T细胞也会对外来组织起反应,例如皮肤移植物和移植 官。
官。