American styling differs from functionalism for its faddism and styling.
与功能主义不 ,
,
 设计追求式
设计追求式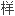 ,引导消费,形
,引导消费,形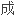

 的独有特点。
的独有特点。
声明:以上例句、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。

 Crash Course
Crash Course  英语
英语 

 Crash Course
Crash Course 

 Crash Course
Crash Course 

 Crash Course
Crash Course 

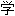 Crash Course
Crash Course 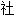

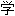 Crash Course
Crash Course 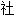

 Crash Course
Crash Course 

 Crash Course
Crash Course 

 Crash Course
Crash Course 

 Crash Course
Crash Course 

 Crash Course
Crash Course  人-文艺
人-文艺 

 Crash Course
Crash Course Now that we understand a little more about the different scales that sociology works on, we can turn to its main theoretical paradigms, of which there are three: There’s structural functionalism, conflict theory, and symbolic interactionism.
现在,理解了

 研究中的宏观和微观层面,我们可以来说说
研究中的宏观和微观层面,我们可以来说说

 中最主要的三个理论模型了:它们是结构功能论,
中最主要的三个理论模型了:它们是结构功能论,

 突论,和符号互动论。
突论,和符号互动论。
Anyone who loves sightseeing will be in paradise as you can choose from palaces, churches, town squares, and so much more However, the best place to visit in the city is Villa Tugendhat, a fantastic example of functionalism.
任何热爱观光的人都 置身
置身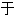 天堂,因为您可以从宫殿、教堂、城镇广场等等中选择。 然而,这座城市最好的游览地点是图根哈特别墅 (Villa Tugendhat),它是功能主义的绝佳典范。
天堂,因为您可以从宫殿、教堂、城镇广场等等中选择。 然而,这座城市最好的游览地点是图根哈特别墅 (Villa Tugendhat),它是功能主义的绝佳典范。