Purpose To evaluate the feasibility and superiority of the catarct ultrasonic emulsification, artificial lens implantation united micro trabecula resection adopt surface anesthescia.
评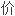
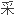 用表面麻醉的白内障超声乳化,人工
用表面麻醉的白内障超声乳化,人工 状体植入联合显微小梁切除术的可
状体植入联合显微小梁切除术的可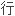
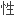 、
、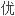 越
越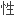 。
。
声明:以上例句、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。