The conjugates of the present invention also exhibit an extended half-life in vivo compared to the corresponding unconjugated cytokine.
相对于未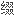 合的
合的

 子、趋化
子、趋化 子、生长
子、生长 子和多肽激素,本发明的
子和多肽激素,本发明的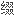 合物也在体内和体外显示出延长的半衰期。
合物也在体内和体外显示出延长的半衰期。
声明:以上例句、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。